Lots of devices were working via copper cables before which makes us really crazy ! After network fiber optic cable invented, our networks began to increase their speeds too. We will examine this crazy technology for you step by step.
Advantages Of Network Fiber Optic Cable
- Extremely high bandwidth
- Smaller-diameter, lighter-weight cables
- Lack of crosstalk between parallel fibers
- Immunity to inductive interference
- High-quality transmission
- Low installation and operating costs
Network Fiber Optic Cable Structure
Core
Thin glass center of the fiber where the light travels
Cladding
Outer optical material surrounding the core that reflects the light back into the core
Coating
Plastic coating that protects the fiber from damage and moisture

Network Fiber Optic Cable Types
G.651 – MMF – Multi-mode fiber
- Large(r) core: 50-62.5 microns in diameter
- Transmit infrared light (wavelength = 850 to 1,300 nm)
- Light-emitting diodes
G.652 – SMF – Single mode fiber
- Small core: 8-10 microns in diameter
- Transmit laser light (wavelength = 1,200 to 1,600 nm)
- Laser diodes
Internal Reflection Of Fiber
Concept
Light travels through the core constantly bouncing from the cladding
Distance
A light wave can travel great distances because the cladding does not absorb light from the core
Signal degradation
Mostly due to impurities in the glass
ATTENUATION AS FUNCTION OF WAVELENGTH
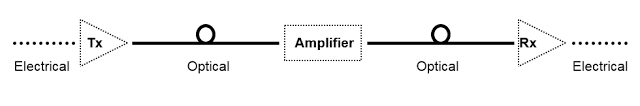
Network Fiber Optic Cable Relay System
Optical transmitter
Produces and encodes the light signal
Optical amplifier
May be necessary to boost the light signal (for long distances)
Optical receiver
Receives and decodes the light signal
Optical fiber
Conducts the light signals over a distance
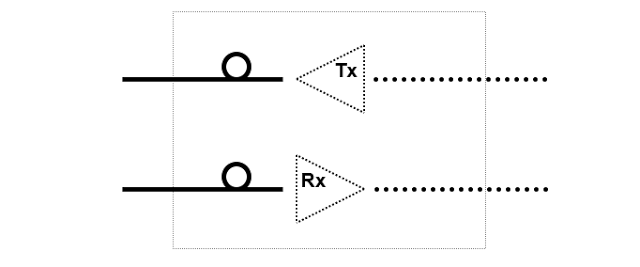
WHAT IS A TRANCIEVER ?
A transmitter and a receiver in a single housing
Practical implementation:
Transceivers typically come as SFP small-Form-factor Pluggable unit
Network Fiber Optic Cable Connectors

Properties
- Good alignment/correct orientation
- Present at the termination point of the fiber
- Always introduce some loss
Connector types
- Amount of mating cycles
- LC, FC, SC, …
Color code
- APC – green
- PC – blue
Joining Fibers – Splices
Mechanical splicing
- Aligning and orienting the fibers, then clamp the fibers in place.
Fusion splicing
- Aligning and orienting the fibers, then fuse (melt) the fibers.
- Using an electric arc.



