In this article, we will deeply examine the wonderful protocol : IGMP ! First of all we need to find that answer who the hell is this guy, what is IGMP ? Let’s take a look at.
IGMP is used to dynamically register individual hosts in a multicast group on a particular LAN.
IGMP Hosts
Hosts identify group memberships by sending IGMP messages to their local multicast router.
IGMP Routers
Routers listen to IGMP messages and periodically send out queries to discover which groups are active or inactive on a particular subnet.
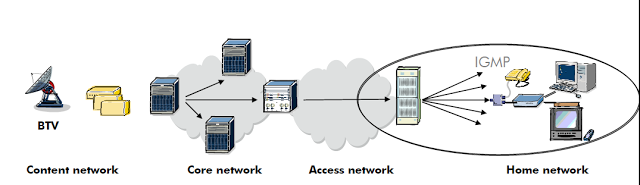
Like ICMP, IGMP is considered part of the IP layer.

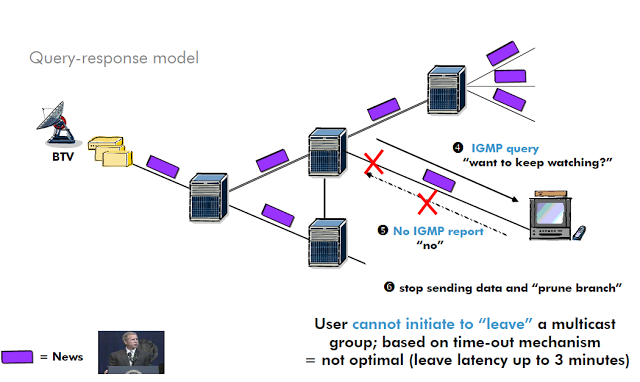
There are different versions of Internet Group Management Protocol ( IGMP ) .IGMPv1 query / response model = age out mechanism, not responding to queries (latency 3 minutes). IGMPv2 introduction of join / leave messages, group specific queries .IGMPv3 source specific query can contain several responses in one report , join and leave for different streams can be in the same message.
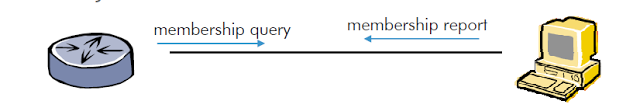
IGMPv1 (RFC1112)
- IGMPv1 = query / response model
- Age out mechanism
- No “leave”-messages.
- (latency 3 minutes)

IGMPv2 (RFC2236)
- Leave messages
- Group specific queries

IGMPv3 (RFC 3376)
- Source specific queries
- Several records per report ( IP SA can be 0.0.0.0 )
- Routers must accept this!
- Info per group record: ( record type:– current state (include /exclude mode– changes (source /mode)
- MC group address
- Source IP-addresses (source = rendez vous point )




Multicast Routing
Router to Router – PIM DM/SM, DVMRP, MOSPF etc.
Client to Router – IGMP (internet group management protocol) version 1,2,3
Multicast Control Termination (MCT) – entity which terminates the IGMP signaling which is used to initiate channel zapping; this protocol is initiated within the customer device (usually a STB) when channel changes are requested
Multicast Engine (ME) – entity which actually copies the stream in order that multiple users can view the same content. Depending upon the architecture the ME function may be done in more than one place.
Static MC stream : MC stream sent/available on switch no matter if there is a subscriber or not

IGMP SNOOPING / PROXY FUNCTIONALITY
L2 boxes like switches are basically unaware of L3
Multicast streams travel through as broadcast traffic (because switches can’t learn multicast addresses (GDA)). Adding IGMP (L3) intelligence to switch will inhibit broadcast Switch will forward multicast stream only to those ports on which it received an IGMP Join message.
IGMP snooping : Monitoring passively the IGMP messages passing by and then taking appropriate actions for setting up multicast branches IGMP proxy Messages do not pass transparently through .
IGMP proxy : Acts as a router and can terminate and generate IGMP messages.

