Most of us using mobile devices such laptops, tablets, phones etc. And today, Wireless LAN ( WLAN ) is a very important part of network design.
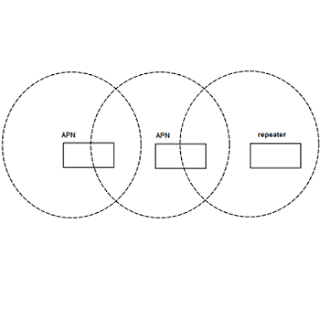
Here is a simple topology example for Wireless LAN ( WLAN ). Simply clients are connected to APN ( Access Points ) on wireless, and APN’s are connected to our network switches. Access points work as a “hub” ( Shared signal and half duplex) and they use unlicensed bands of the RF. A wireless network design should be made very carefully , because interference problem may occur because of the walls and etc. As you can see from the figure above, RF areas should overlap like %15 , repeaters should overlap like %50. Border APNs should use different channels.
ROAMING

Roaming is a great feature that provides an uninterrupted connection. To provide roaming, you should use same SSID , VLAN and subnets on the APNs. So that even if you go to another APNs area you connection won’t interrupt. This is known as Layer-2 roaming, and there is also Aka Mobile Roaming, which is known as Layer-3 roaming.

If you prefer to make a WLAN topology like this, you can create muliple security levels, multi subnets and multi access denies.
FREQUENCIES, 802.11 AND SECURITY STANDARDS
As we talked above Access points use unlicensed bands of the RF. They are :
- 900 mhz : 902-928
- 2,4 ghz : 2.4 – 2.483
- 5 ghz : 5.150 – 5.350
Here is what we need to know about RF :
- RF waves are absorbed and effected from metals or etc. easily.
- High data rates go to shorter distances.
- High frequencies have much more data.
- High frequency go to shorter distances.
And here is the types of the 802.11 standard. They support different channels and speeds.
802.11B
–11 Mbps
–3 channels
802.11G
–54 Mbps
–3 channels
802.11A
–54 Mbps
–12 to 23 channels
WIRELESS SECURITY
Here is the security methods we use for WLANs. You can see these steps while configuring your xDSL modem’s wireless connection easily 🙂
– WEP
– 802.1x EAP
– WPA ( Encyription of WPA is TKIP )
– 802.11 (WPA2) ( AES is used for newer APNs )
WIRELESS HARDWARE
Autonomous APs
–Stand alone IOS based
–Central control via wireless Domain Services (WDS)
–Managed via WLAN Solution Engine (WLSE)
LIGHT WEIGHT APs
–Server oriented and can not be configured manually.
–Central control via Wireless LAN controller ( gets configuration from here )
-Can be managed via Wireless control system (WCS) ( optional )
–WLC manages all the connection and APs just moves the packets as a dummy terminal.
-Known as split-MAC design.
WLC TYPES
2100:
– Designed for 5 MB traffic and supports up to 6 access points.
4400:
– Supports 12, 25 or 50 APs ( 4402 )
– Cisco 1130 and 1240 AG is the most used APs. ( indoor APs )
– Cisco 1300 and 1400 are the outdoor APs. Especially 1400 supports long distances.
* It’s offered that you use POE ( Power over Ethernet ) switches with supported APs.
ANTENNA TYPES
There are three types of antennas that is used for WLAN devices :
– Omni Directional ( Single side spread from the access point )
– Directional
– Yagi ( Can be adjusted )

