Let’s do some routing and we are getting started with EIGRP : Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol. First we need to answer the question “what is eigrp” ? EIGRP is a dynamic routing protocol and provides us some great features. It uses “DUAL” algorithm to find the best path which is found by Dr. J.J. Garcia-Luna Aceves. EIGRP was a Cisco proprietary protocol like HSRP and GLBP before but it is not anymore. ( Check this link for more info )
WHY WE USE EIGRP ?
* Keeps Backup Routes
There are some key features that we need to know about this protocol. First key feature of EIGRP is that the protocol keeps backup routes. If a network is down, RIP asks the other routes to neighbors, OSPF keeps the backup routes on its topology database and etc. If primary route is down and if we are using OSPF, SPF algorithm is worked and backup route is found. But if we are using EIGRP and if primary route is down, “feasible successor” replaces it immediately.
* Flexibility In Summarization
Summarizing is a really great feature that helps your routing table to decrease. If you are using OSPF, just two routers can make summarization ( ABR and ASBR ). But if you are using EIGRP , you can make summarization on each interface.
* Unequal Cost Load Balancing
All other protocols are making equal load balancing, but EIGRP can make unequal load balancing. This is a great feature of EIGRP Load Balancing.That means you can send 2 packets from one link while sending 1 packet from the other link.
EIGRP TABLES AND TERMINOLOGY
* Neighbor Table
Neighbor table includes all neighbors that is directly connected to router using EIGRP. Neighbors exchange their routing tables and this process is made by “hello” packets while it is made by multicast on RIP.
* Topology Table
Topology table includes successor , feasible successor and all other paths going to the target network.
* Routing Table
Routing table includes best paths for the target network. There are some other terminologies that we need to know in here, one of them is Active Route which means there is a down network and router is actively trying to find a path for it. Passive Route means everything is OK and there is not a down network.
* Feasible Distance And Advertised Distance ( FD and AD )

Feasible distance is the distance of a spesific way to the router.
Advertised distance is the distance of a route to the neighbor router.
Successor= Primary Route ( Route which is used firstly )
Feasible Successor= Backup Route ( Backup path if the primary route fails )
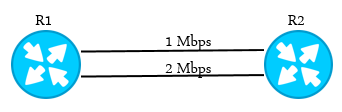
For the figure above, let’s check what is feasible distance and advertised distance.
For the path on the left side :
For 10.1.2.0 FD=110(R1)
For 10.1.2.0 AD=10(R1)
For the other path :
FD=210(R1)
AD=10(R1)
Note : Because of 110 is less 210 the path on left side is primary route.
Note : If a path is wanted to be chosen as “feasible successor” , AD < FD of successor condition should be provided ! If a successor can’t be found because of this condition is not being provided, R1 sends query messages and if still R1 can’t find a better path it adds this routes to its routing table.
EIGRP MESSAGE TYPES
There are 5 eigrp message types about EIGRP neighborhood relationship :
* Hello : Hello packets establishes the neighborhood. ( sent to 224.0.0.10 )
* Update : Update packets are sent if only there is a change in network topology.
* Query : Query is the packet that asks if network occurs on neighbor or not.
* Reply : Reply packet is the answer of the query packet.
* ACK : Acknowledges the query, update and reply packets.
EIGRP METRIC CALCULATION
There are 5 variables that effect eigrp metric calculation :
- Bandwith ( 107/BW )
- Delay ( Milisecond )
- Reliability
- Loading
- MTU
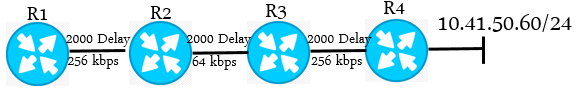
You can calculate the metric for the figure above with this formula ( 256 x ( Lowest BW + All delays )
= 256 . (107/64 + 6000)
