After overview of EIGRP , it is time to take a look at EIGRP configuration. EIGRP configuration is really awesome and not so hard if you compare with OSPF or etc. Let’s take a look to figure below and configure this topology via EIGRP step by step.
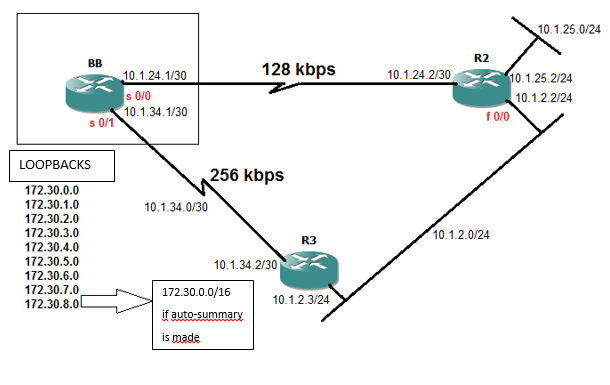
- Configure the network above with EIGRP using Autonomous system number 90. Use the spesific wildcard masks for R2 and R3. Additionally EIGRP shouldn’t work as a classful routing protocol. BB router has a static route to 192.168.1.0/24 network, R2 and R3 should learn it without redistribution.
- R2 and R3 , should have a default route targetting to 192.168.1.0/24 network without using static routing. Make the necessary configuration.
- EIGRP neighborhood shouldn’t be established on any interface if there are no EIGRP routers.
- BB router should summarize networks between 172.30.0.0 / 172.30.7.255 as a single network.
- BB router should use unequal load balance to reach 10.1.2.0 / 24 network.
BB router:
BB(conf)#router eigrp 90 BB(config-router)#network 172.30.0.0 0.0.255.255 BB(config-router)#network 10.1.0.0 0.0.255.255 (1) BB(config-router)#no auto BB(config-router)#exit BB(config)#ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 null0 BB(conf)#network 192.168.1.0
For the EIGRP configuration we use “router EIGRP AS number” , then we advertise the related networks using the wildcard masks. “no auto” command stops the EIGRP auto summarization. We wrote a static route to directly connected interface to advertise it.
BB(conf)#ip default–network 192.168.1.0 (2) BB(conf)#router eigrp 90 BB(config-router)#passive interface loopback 0-1-2-3.. (3)
Passive Interface Command : Don’t send hello packets from loopbacks but continue to advertise that networks.
BB(conf)#int s0/0 BB(conf-if)#ip summary–address eigrp 90 172.30.0.0 255.255.0.0 (4) BB(conf)#int s0/1 BB(conf-if)#ip summary–address eigrp 90 172.30.0.0 255.255.248.0 BB(conf)#router eigrp 90 BB(conf-router)#variance 2
Variance command : Helps to make unequal load balancing
R2 ROUTER:
R2(conf)#router eigrp 90 R2(config-router)#network 10.1.2.2 0.0.0.0 R2(config-router)#network 10.1.24.2 0.0.0.0 R2(config-router)#network 10.1.25.2 0.0.0.0 R2(config-router)#no auto R2(config-router)#passive-interface fastethernet 0/1 (3)
Interface addresses are used for the network statements because of the spesific wildcard mask request at the question.
R3 ROUTER:
R3(conf)#router eigrp 90 R3(config-router)#network 10.1.2.3 0.0.0.0 (1) R3(config-router)#network 10.1.34.2 0.0.0.0 R3(config-router)#no auto
*** Let’s see what if we make the configurations on step 4 ( ip summary –address ) for just s 0/0
R2#show ip route D 172.30.1.0/24 via 10.1.2.3 D 172.30.2.0/24 via 10.1.2.3 D 172.30.3.0/24 via 10.1.2.3 D 172.30.4.0/24 via 10.1.2.3 D 172.30.5.0/24 via 10.1.2.3 D 172.30.6.0/24 via 10.1.2.3 D 172.30.7.0/24 via 10.1.2.3 D 172.30.8.0/24 via 10.1.2.3 172.30.0.0/21 via 10.1.24.1 s 0/0
Summarization doesn’t work because there are more spesific routes in the routing table.
*** After configuring on s0/1 too
R2#show ip route D 172.30.0.0/21 via 10.1.2.3 172.30.8.0/24 via 10.1.2.3
*** Let’s see the BB router’s routing and EIGRP topology table after the configuration step 1.
BB#show ip route C 172.30.2.0 is directly connected C 172.30.3.0 is directly connected C 172.30.4.0 is directly connected C 172.30.5.0 is directly connected C 172.30.6.0 is directly connected C 172.30.7.0 is directly connected C 172.30.8.0 is directly connected D 10.1.2.0/24 via 10.1.34.2 // This path has better bandwith // D 10.1.25.0/24 via 10.1.34.2
BB#show ip eigrp topology
10.1.2.0/24 , 1 successors FD is 10537472
via 10.1.34.2 (10537472/281600) ,serial 0/1 // This is successor because has lower FD //
via 10.1.24.2 (20537600/281600) , serial 0/0 // This is feasible successor for 10.1.2.0 //
// FD : 20537600 , AD 281600 //
10.1.25.0 …. 1 successor
*** Let’s see the BB router’s routing table after configuration step 5. ( Variance )
BB#show ip route D 10.2.2.0/24 [90/10537472] via 10.1.24.2 serial 0/1 [90/20537600] via 10.1.24.2 serial 0/0
That refers to while two packets are passing through serial 0/1 , one packet is passing through serial 0/0 interface.

