PSTN voice calls require 64 kbps bandwith, VOIP voice calls require 8 kbps bandwith. Here is a good entry for “why we use VOIP (Voice Over IP) ? ” question. VOIP is a great way for the corporates to make their calls really cheaper way and to keep their networks flexible. Let’s see a voip topology first and talk about it :

You can see two telephones of Jack and Helen. Jack’s phone number is 2002, Hellen’s phone number is 2003. Both phones are connected to same switch and switch is connected to a “Call Manager” which forwards the call requests. When Jack wants to talk with Hellen, he lifts his handset first. As soon as he lifts the handset, call manager receives the “skinny protocol” and sends Jack a dial tone. After Jack dials 2003 to connect with Helen. Call manager keeps the phone numbers and IP addresses on its own table and routes Jack’s call to Helen’s phone and they start to talk via RTP ( real time protocol ). This is simply how a voip call occurs. As you can see on the figure above, PSTN network is also connected to our VOIP network because of to make and receive calls between VOIP and PSTN.
VOIP VLAN STRUCTURE : DUAL VLAN

In the real life, we use different VLANs to seperate voice and data traffic. As you can see from the figure above, switch is directly connected to IP phone and IP Phone’s “PC” ethernet is connected to PC directly. IP phone is in VLAN 100 and PC is on VLAN 200. We seperate voice and data traffice because of easier management ( If just IP phones are not working, you can check VLAN 100 configs ! ) and security issues. VLAN 100 is named as “voice vlan”.
Voice VLAN Configuration :
SWITCH_A(conf)#interface Fa 0/5 SWITCH_A(conf-if)#switchport mode access SWITCH_A(conf-if)#switchport access vlan 200 SWITCH_A(conf-if)#switchport voice vlan 100
There you can see how we configure our VOIP (Voice Over IP) topology above. I wanna tell you a trick again, on some IP phones you can use just data vlan and don’t create any voice VLANs and they work again over data VLAN. But in some IP phones, you should create a voice VLAN, if you don’t do it they won’t work.
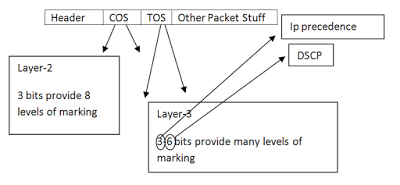
You can also use QOS for the VOIP calls too. Here you can see a QOS packet below, please pay attention that COS ( Class of service ) works at Layer-2 while TOS ( Type of service ) is working at Layer-3 ) :
There we can configure our f0/5 port to give priority to the IP phone calls :
SWITCH_A(conf)#interface Fa 0/5 SWITCH_A(conf-if)#mls qos trust cos SWITCH_A(conf-if)#mls qos trust device cisco-phone SWITCH_A(conf-if)#auto qos voip cisco-phone

