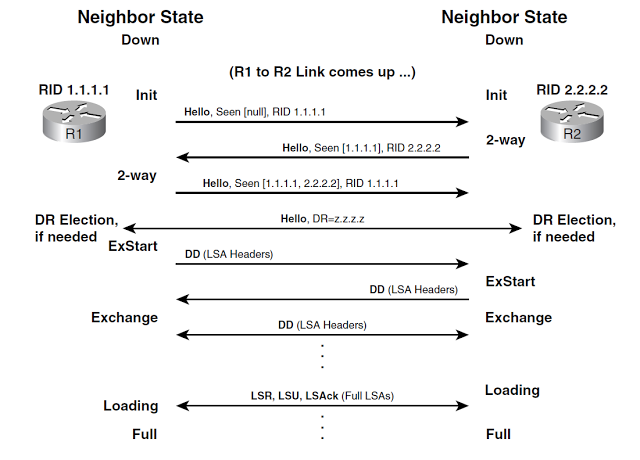
After OSPF Basics it is time to look at “OSPF Neighbor States”. In this article, we will review to step by step OSPF neighbor adjacency. May be you saw the image below before, but we will examine it deeply.
1) First step of “OSPF neighbor states” is determining the “Router ID”s. Both routers determine their router ID’s firstly. Router ID is the biggest IP address of active interfaces. But if you attached an IP address to a loopback interface, router ID is the IP address of this interface.
– Router ID changes only if you restart OSPF process or reboot the router.
– Router ID can be hard coded as “router-id x.x.x.x” manually.
2) Interfaces are added to link state database using “network x.x.x.x a.a.a.a” command.
3) Send hello messages from the choosen interfaces.
– Hello messages are sent once in 10 second in Broadcast or P2P networks. But if you are working on NBMA network, ( F/R or ATM etc. ) hello messages are sent once in 30 second.
Hello message includes these informations :
-Router ID
-Hello-Dead timer(*)
-Network Mask(*)
-Area id(*)
– Neighbors
-Router Priority
-DR/BDR IP
-Authentication password(*)
(*) signed informations should be same on each router to establish a OSPF neighborship !!!
4) Other router receives the hello message and checks the (*) signed properties. This state is named “init state” of the OSPF neighbor states.
5) HIf everything is OK, other router sends “Reply Hello” packet and joins the “2 way state” which DR and BDR selection is made.
* Am I in your neighbor list of your hello packet ?
-Yes: Reset your dead timer.
-No: Add me as a new neighbor as told in step 6.
6) Master – slave relationship is determined between to routers. This is “exstart state”. Link state database exchange begins in this state between two routers. Master router is the router who sends its link state database first.
*Master selection is made due to priority value. If both routers’ priority value is same, the router which has higher router-id is the master router..
*Master router sends “Database Description Packet” (DBD) to slave router. There is a summary of link state database in the DBD packet. After slave router sends “Database Description Packet” (DBD) to master router.
7) DBD packets are acknowledged and OSPF Loading State begins.
* Because of DBD is a summary, slave router demands the all details of the networks that it doesn’t know. This is known as “link state request”. After master router sends the updates. The master router sends the details as slave did and slave sends the updates.
* After all these steps 2 routers have the same link state database and neighbor adjacency is established. This state is “Full State”
*OSPF neighbor states are very important to understand the basics of the protocol !